- Home
- About IGU's
- Breakage
- Mechanical strokes
- Surface pressure break V (explosion fragmentation) – multi-level safe glass
Surface pressure break V (explosion fragmentation) – multi-level safe glass
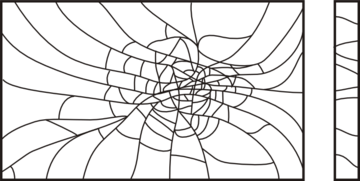
| Type of glass |
Laminated glass, also glass pack. |
|---|---|
| Examples |
Very big load due to the temperature, air pressure, and / or height differences between the glass pack production and installment places; Filled too cold gas and a big gap in the glass pack; Explosion. |
| Beginning |
Edge crack angle in all directions, not upright; not visible centre of fragmentation; Transition angle not upright; There are no curvilinear cracks by the glass edge. |
| Lines of process |
From the middle of the arc form; No opening; Break scheme with cross cracks that increase towards the gap in the middle of the glass; Direct, often round break lines. |
| End |
From the middle of the glass always till the angle or near the angle of the glass. |
| Other features |
Surface curvilinear fragmentations; in the convex pieces of glass (usually the sub atmospheric pressure in the gap) – external curvilinear cracks, in the convex pieces of glass (overpressure in the gap) in the side of the gap, thus it is possible to recognize whether the break occurred due to the overpressure or due to the sub atmospheric pressure; With the increasing load, the number of fragmentations also increases; In the single glass curvilinear cracks in the load side; In the case of explosion, curvilinear cracks in the load side. |










